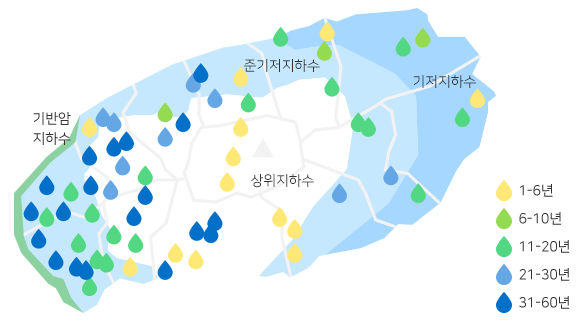
Jeju Island’s groundwater resources can be categorized as high-level, parabasal, basal, and basement groundwaters depending on its interaction with freshwater and seawater, underground geological structure, and water level.
- High-level groundwaterHigh-level groundwater occurs when rain water seeps into the ground because of gravity until it meets low-permeability layers such as dense layers of rocks or clay and cannot go any deeper but flows along with the layers
- Parabasal groundwaterParabasal groundwater is a type of groundwater to which Ghyben-Herzberg equation does not apply as seawater cannot intrude fresh groundwater aquifer because Seogwipo layer blocks the contact
- Basal groundwaterBasal groundwater is a type of groundwater that exists in the form of a fresh water lens above salt water layer because of the difference in density between saltwater and freshwater (Ghyben-Herzberg ratio)
- Basement groundwaterBasement groundwater can be found deep in the ground. It occurs from rain water and is within effective porosity of fractured zones or joints in bedrock such as Daebo granite (aged 172.4±5.2Ma) and welded tuff in the bottom of U-shaped layer (unconsolidated layer) from an unknown period
Jeju’s groundwater is 23-years-old on average, but groundwater ages vary depending on the area. Relatively older groundwater is in the west part of Jeju while the average groundwater age is 13 years in the southern part of the island, indicating a shorter cycle of groundwater circulation. The figure is 21 years and 19 years respectively for the northern and eastern parts of the island.


 EN
EN

